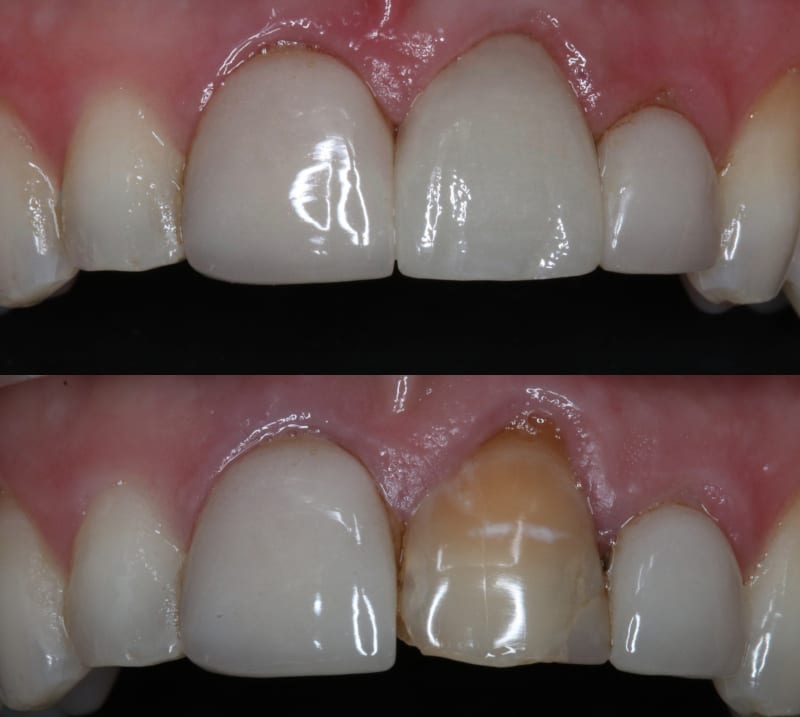
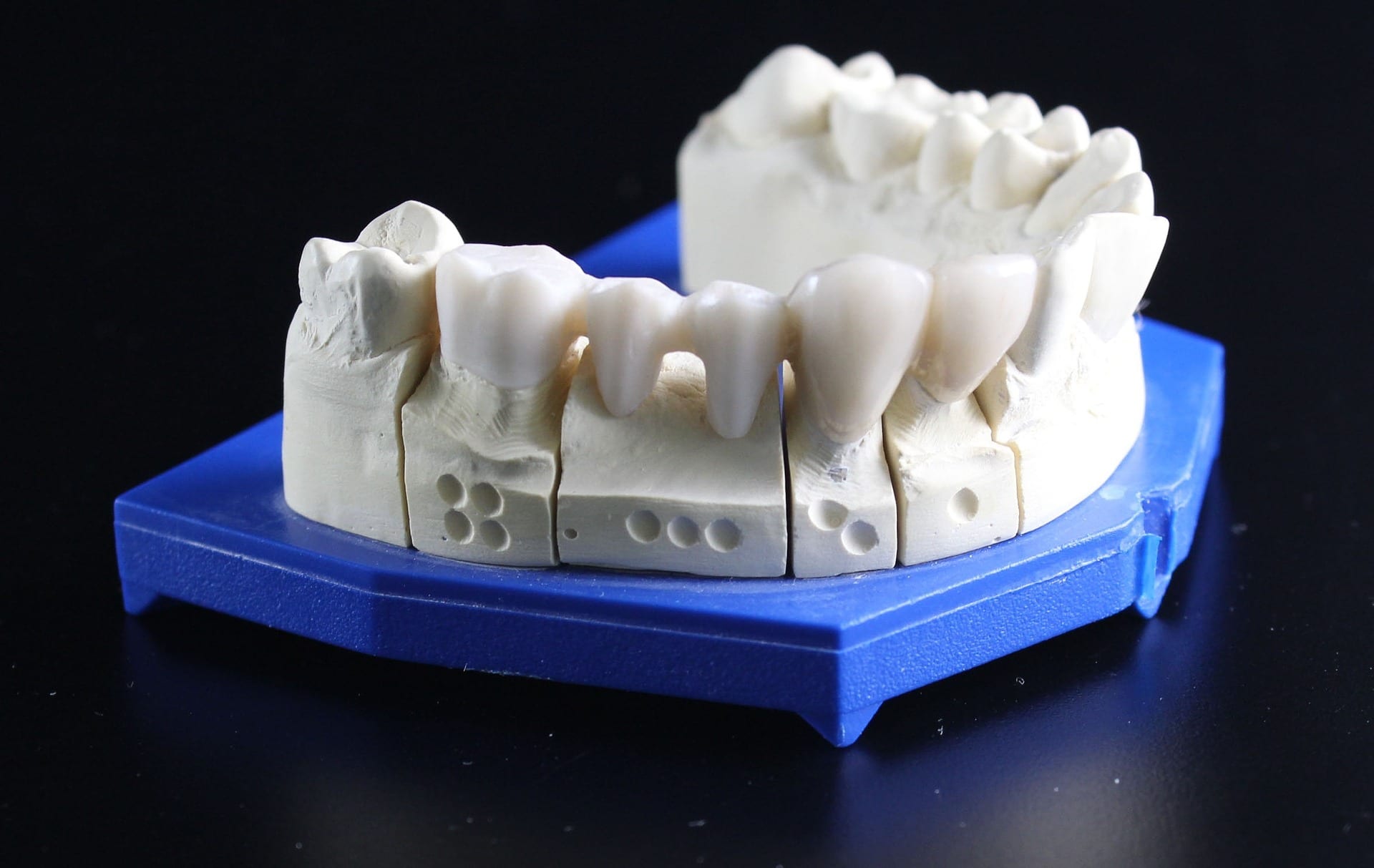
Dental implants
Dental implants in Poland
Dental implants are an increasingly popular and effective solution for replacing missing teeth and restoring your smile. Unlike traditional dentures or bridges, dental implants are a long-lasting solution that can look and feel like your natural teeth.
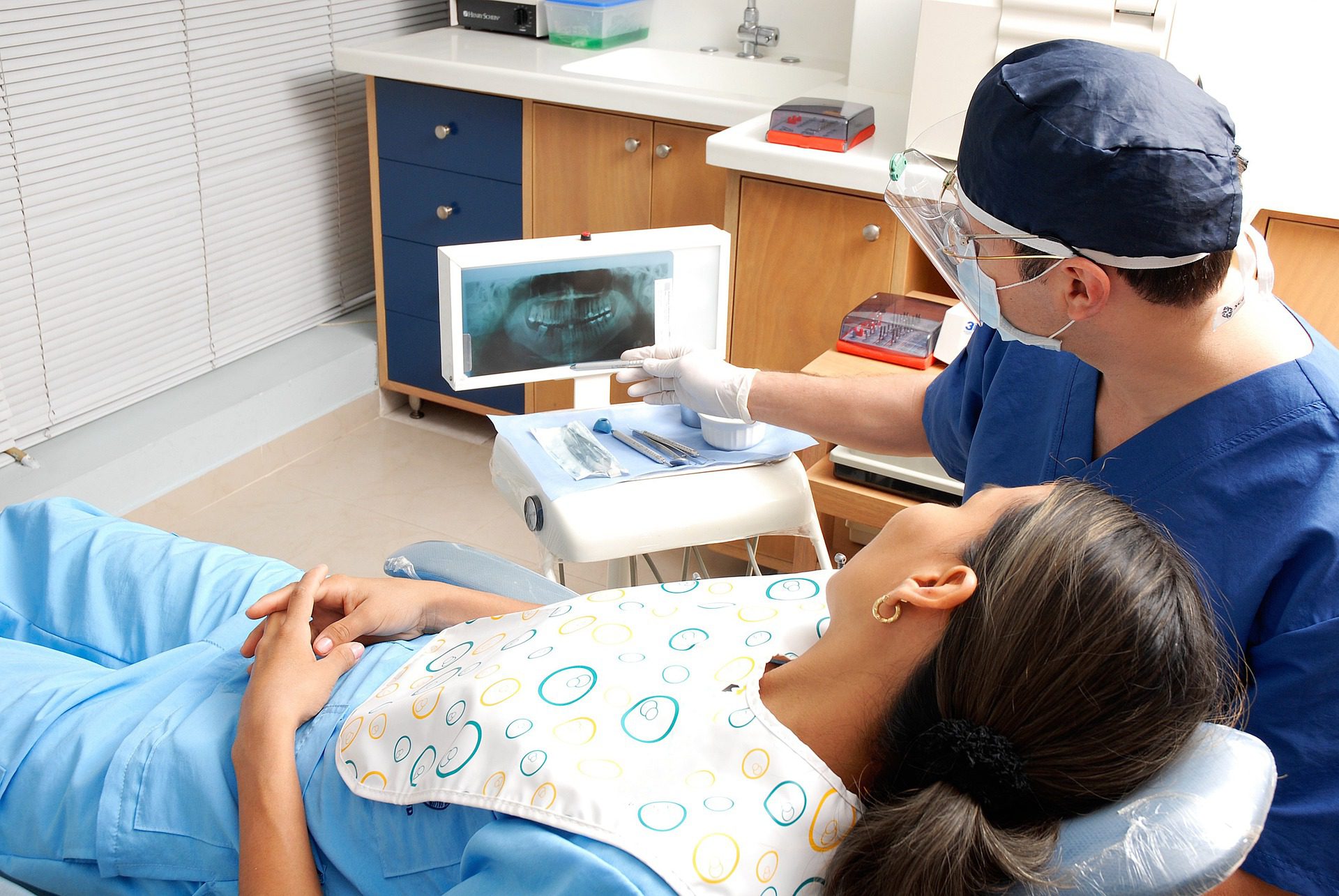
The first step in the dental implant process is a consultation with your dentist. During this appointment, your dentist will evaluate your oral health, take X-rays, and determine if you are a good candidate for dental implants. If you are a candidate, the next step is the implant surgery. During the surgery, a small titanium post is inserted into your jawbone, which acts as the root of your new tooth. The post is then allowed to fuse with the bone, which can take several months.
Once the post has fused with the bone, a connector called an abutment is attached to the post. This connector serves as the base for your new tooth, which is then attached to the abutment. The new tooth is custom-made to match your natural teeth in size, shape, and colour, ensuring a natural and comfortable fit.
Long-lasting solution
One of the primary benefits of dental implants is that they are a long-lasting solution. With proper care and maintenance, dental implants can last for many years, making them a cost-effective solution for restoring your smile. Additionally, dental implants can help prevent bone loss in the jaw, which can occur when teeth are missing, and can also improve your ability to chew and speak properly.
While dental implants are a safe and effective solution for most patients, there are some potential risks and complications to be aware of. These can include infection, nerve damage, or implant failure. However, with proper care and maintenance, the risk of these complications is low.
Due to the cost in the UK, many Brits decide to have their dental implants in Poland where they can save up to 70% on UK prices.
Popular dental implants in Poland
All-on-4 / All-on-6 – This is a popular procedure in Poland where 4-to-6 dental implants are placed in the upper or lower jawbone to serve as a support for a permanently fixed (non-removable) ceramic bridge made of 10-14 custom-made ceramic crowns.
What is a dental implant?
A dental implant is a surgical component that interfaces with the bone of the jaw or skull. It supports a dental prosthesis such as a crown, bridge, denture, facial prosthesis or to act as an orthodontic anchor. It is a fairly complicated and lengthy procedure requiring a minimum of two visits so you should bear this in mind when having your dental implants in Poland.
Osseointegration
The basis for modern dental implants is a biologic process called osseointegration, in which materials such as titanium form an intimate bond to bone.
The implant fixture is first placed so that it is likely to osseointegrate, then a dental prosthetic is added. A variable amount of healing time is required for osseointegration before either the dental prosthetic (a tooth, bridge or denture) is attached to the implant, or an abutment is placed which will hold a dental prosthetic.
Success or failure
Success or failure of implants depends on the health of the person receiving the treatment, drugs which affect the chances of osseointegration, and the health of the tissues in the mouth.
The amount of stress that will be put on the implant and fixture during normal function is also evaluated. Planning the position and number of implants is key to the long-term health of the prosthetic since bio-mechanical forces created during chewing can be significant.
Positioning
The position of implants is determined by the position and angle of adjacent teeth, by lab simulations or by using computed tomography with CAD/CAM simulations and surgical guides called stents. The prerequisites for long-term success of osseointegrated dental implants are healthy bone and gingiva. Since both can atrophy after tooth extraction, pre-prosthetic procedures such as sinus lifts or gingival grafts are sometimes required to recreate ideal bone and gingiva.
Fixed or removable
The final prosthetic can be either fixed, where a person cannot remove the denture or teeth from their mouth, or removable, where they can remove the prosthetic. In each case an abutment is attached to the implant fixture. Where the prosthetic is fixed, the crown, bridge or denture is fixed to the abutment either with lag screws or with dental cement. Where the prosthetic is removable, a corresponding adapter is placed in the prosthetic so that the two pieces can be secured together.
Risks & complications
The risks and complications related to implant therapy divide into those that occur during surgery (such as excessive bleeding or nerve injury), those that occur in the first six months (such as infection and failure to osseointegrate) and those that occur long-term (such as peri-implantitis and mechanical failures).
In the presence of healthy tissues, a well-integrated implant with appropriate biomechanical loads can have 5-year plus survival rates from 93 to 98 percent and 10 to 15-year lifespans for the prosthetic teeth. Long-term studies show a 16- to 20-year success (implants surviving without complications or revisions) between 52% and 76%, with complications occurring up to 48% of the time.
Medical uses
The primary use of dental implants is to support dental prosthetics. Modern dental implants make use of osseointegration, the biologic process where bone fuses tightly to the surface of specific materials such as titanium and some ceramics. The integration of implant and bone can support physical loads for decades without failure.
For individual tooth replacement, an implant abutment is first secured to the implant with an abutment screw. A crown (the dental prosthesis) is then connected to the abutment with dental cement, a small screw, or fused with the abutment as one-piece during fabrication. Dental implants, in the same way, can also be used to retain a multiple tooth dental prosthesis either in the form of a fixed bridge or removable dentures.
An implant supported bridge (or fixed denture) is a group of teeth secured to dental implants so the prosthetic cannot be removed by the user. Bridges typically connect to more than one implant and may also connect to teeth as anchor points. Typically, the number of teeth will outnumber the anchor points with the teeth that are directly over the implants referred to as abutments and those between abutments referred to as pontics.
Implant supported bridges attach to implant abutments in the same way as a single tooth implant replacement. A fixed bridge may replace as few as two teeth (also known as a fixed partial denture) and may extend to replace an entire arch of teeth (also known as a fixed full denture). In both cases, the prosthesis is said to be fixed because it cannot be removed by the denture wearer.
A removable implant supported denture (also an implant supported overdenture) is a type of dental prosthesis which is not permanently fixed in place. The dental prosthesis can be disconnected from the implant abutments with finger pressure by the wearer. To enable this, the abutment is shaped as a small connector (a button, ball, bar or magnet) which can be connected to analogous adapters in the underside of the dental prosthesis. Facial prosthetics, used to correct facial deformities (e.g., from cancer treatment or injuries) can use connections to implants placed in the facial bones. Depending on the situation the implant may be used to retain either a fixed or removable prosthetic that replaces part of the face.
TADs
In orthodontics, small diameter dental implants, referred to as Temporary Anchorage Devices (or TADs) can assist tooth movement by creating anchor points from which forces can be generated. For teeth to move, a force must be applied to them in the direction of the desired movement. The force stimulates cells in the periodontal ligament to cause bone remodelling, removing bone in the direction of travel of the tooth and adding it to the space created. In order to generate a force on a tooth, an anchor point (something that will not move) is needed.
Since implants do not have a periodontal ligament, and bone remodelling will not be stimulated when tension is applied, they are ideal anchor points in orthodontics. Typically, implants designed for orthodontic movement are small and do not fully osseointegrate, allowing easy removal following treatment.
Composition
A typical conventional implant consists of a titanium screw (resembling a tooth root) with a roughened or smooth surface. The majority of dental implants are made out of commercially pure titanium, which is available in four grades depending upon the amount of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen and iron contained.
In conclusion, dental implants are an excellent solution for replacing missing teeth and restoring your smile. If you’re considering dental implants, it’s essential to work with a qualified and experienced dentist who can guide you through the process and provide you with the best possible care. With proper care and maintenance, dental implants can provide a long-lasting solution that can improve your quality of life and restore your confidence in your smile.
FAQs about Dental Implants
How much are dental implants in Poland?
Prices vary from clinic to clinic; however, as a general guide: A single tooth implant in Poland will cost from £550, the cost in the UK is around £2,000. Full mouth implants in the UK are £7,000 – £28,000, in Poland the cost is £4,000 to £9,000.
What are All-on-4 dental implants?
All-on-4 is a procedure where 4 dental implants, depending on bone availability (i.e., volume, density, etc.) are placed in the upper or lower jawbone to serve as a support for a permanently fixed ceramic bridge made of 10-14 custom-made ceramic crowns.
How much do All-on-4-dental implants cost in Poland?
All-on-4 dental implants cost from £5200 – £7000 in Poland. In the UK, the cost is from £9500 – £16000.
Are dental implants removable?
The final prosthetic can be either fixed, where a person cannot remove the denture or teeth from their mouth, or removable, where they can remove the prosthetic.
What are the risks with dental implants?
The risks and complications related to implant therapy divide into those that occur during surgery (such as excessive bleeding or nerve injury), those that occur in the first six months (such as infection and failure to osseointegrate) and those that occur long-term (such as peri-implantitis and mechanical failures).
How long do dental implants last?
In the presence of healthy tissues, a well-integrated implant with appropriate biomechanical loads can have 5-year plus survival rates from 93 to 98 percent and 10 to 15-year lifespans for the prosthetic teeth. Long-term studies show a 16- to 20-year success (implants surviving without complications or revisions) between 52% and 76%, with complications occurring up to 48% of the time. Many dentists conservatively estimate that implants will last about 25 years.
What is osseointegration?
The basis for modern dental implants is a biologic process called osseointegration, in which materials such as titanium form an intimate bond to bone. The implant fixture is first placed so that it is likely to osseointegrate, then a dental prosthetic is added. A variable amount of healing time is required for osseointegration before either the dental prosthetic (a tooth, bridge or denture) is attached to the implant, or an abutment is placed which will hold a dental prosthetic.