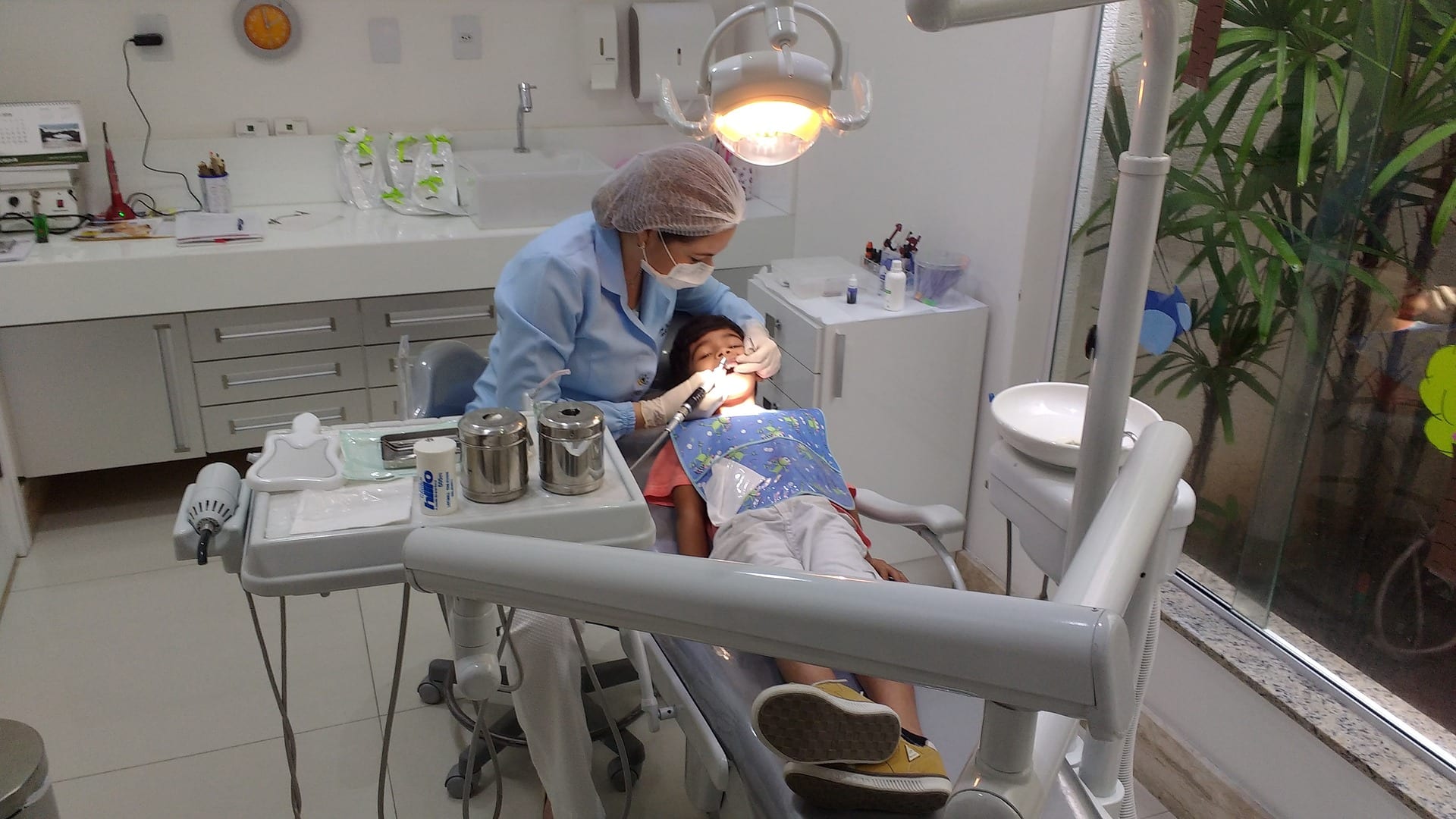
Dental fillings in Poland
A dental restoration or dental filling is a treatment to restore the function, integrity, and morphology of missing tooth structure resulting from caries or external trauma as well as to the replacement of such structure supported by dental implants. This treatment is widely available in Poland. The goal of dental restoration is to improve the function and appearance of the teeth, while also maintaining good oral health.
Types of dental restoration
There are several different types of dental restoration procedures that can be performed, depending on the specific needs of the patient. Some of the most common procedures include:
-
Fillings: This is the most common type of dental restoration, and involves filling a cavity with a material such as composite resin, amalgam, or gold. Fillings are used to restore the function of the tooth and prevent further decay.
-
Crowns: A crown is a cap that is placed over a damaged or weakened tooth to provide support and restore its function. Crowns are typically made from porcelain or metal and can last for many years with proper care.
-
Bridges: A bridge is a dental appliance that is used to replace one or more missing teeth. The appliance is anchored to the adjacent teeth with crowns, and a false tooth or teeth are attached to the bridge to fill the gap.
-
Implants: Dental implants are a permanent solution for missing teeth. They are surgically implanted into the jawbone and serve as a replacement for the root of the missing tooth. Once the implant is securely in place, a crown is attached to the top to provide a natural-looking and functional replacement tooth.
-
Dentures: Dentures are removable appliances that are used to replace multiple missing teeth. They can be full or partial and are designed to fit snugly over the gums.
Regardless of the specific procedure, dental restoration is a critical aspect of maintaining good oral health. When left untreated, dental problems can worsen and lead to more serious health issues such as infections, gum disease, and tooth loss.
If you are experiencing dental issues or have missing teeth, it is important to consult with a dental professional. They can evaluate your needs and recommend the best course of action for restoring your teeth and maintaining your oral health.
In addition to professional dental care, it is also important to practice good oral hygiene at home. This includes brushing and flossing regularly, as well as avoiding sugary foods and drinks that can contribute to tooth decay.

Tooth preparation
Restoring a tooth to good form and function requires two steps:
- preparing the tooth for placement of restorative material or materials
- placement of these materials
The process of preparation usually involves cutting the tooth with a rotary dental hand piece and dental burrs or a dental laser. This is to make space for the planned restorative materials and to remove any dental decay or portions of the tooth that are structurally unsound. If permanent restoration cannot be carried out immediately after tooth preparation, temporary restoration may be performed.
In preparing a tooth for a restoration, a number of considerations will determine the type and extent of the preparation. The most important factor to consider is decay. For the most part, the extent of the decay will define the extent of the preparation, and in turn, the subsequent method and appropriate materials for restoration.
Direct restorations
This technique involves placing a soft or malleable filling into the prepared tooth and building up the tooth. The material is then set hard, and the tooth is restored. The advantage of direct restorations is that they usually set quickly and can be placed in a single procedure. The dentist has a variety of different filling options to choose from. A decision is usually made based on the location and severity of the associated cavity. Since the material is required to set while in contact with the tooth, limited energy (heat) is passed to the tooth from the setting process.
Indirect restorations
In this technique the restoration is fabricated outside of the mouth using the dental impressions of the prepared tooth. Common indirect restorations include inlays and onlays, crowns, bridges, and veneers. Usually, a dental technician fabricates the indirect restoration from records the dentist has provided. The finished restoration is usually bonded permanently with a dental cement. It is often done in two separate visits to the dentist. Common indirect restorations are done using gold or ceramics.
While the indirect restoration is being prepared, a provisory/temporary restoration is sometimes used to cover the prepared tooth to help maintain the surrounding dental tissues.
Removable dental prostheses (mainly dentures) are sometimes considered a form of indirect dental restoration, as they are made to replace missing teeth.
Restoration using dental implants
Dental implants are anchors placed in bone, usually made from titanium or titanium alloy. They can support dental restorations which replace missing teeth. Some restorative applications include supporting crowns, bridges, or dental prostheses.
Overall, dental restoration is an essential part of maintaining good oral health and can help to improve both the function and appearance of your teeth. Whether you need a filling, a crown, an implant, or another type of dental restoration, working with a trusted dental professional can help you achieve the best possible results.
FAQs about Dental Restorations
What is Restorative dentistry?
Restorative dentistry is the study of diagnosis of and management of diseases of the teeth and their supporting structures. It includes the rehabilitation of the dentition to the functional and aesthetic requirements of the patient e.g., replacing of missing or damaged teeth. Fillings, crowns, bridges and implants are common restorative solutions. The aim is to bring back your natural smile and prevent future oral health issues.
How much do fillings cost in Poland?
White fillings cost around £50 with high aesthetic fillings costing from £140. This is much cheaper than the UK (50-70%).